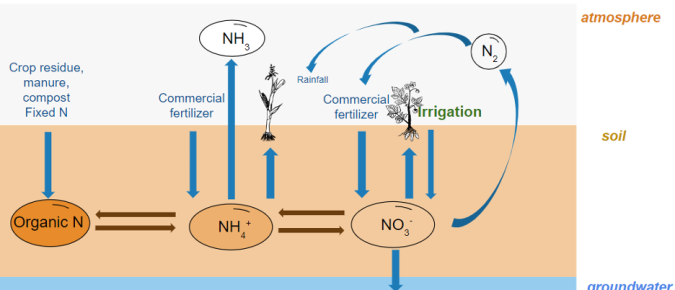
In this article, we will discuss the presence of nitrate in irrigation water and opportunities to budget nitrogen in irrigation, to make farms more efficient in using nitrogen and reduce over-fertilization which in turn will protect groundwater.
The use of tile drainage is becoming more popular in Wisconsin. Installing a tile drain system can be a great tool to dry soil out faster, improving the timeliness of field operations throughout the cropping season. However, how do tile systems influence water movement off of the field, and what are the water quality implications?
Guolong Liang, outreach specialist for the Agriculture Water Quality Program of Extension in the Central Sands of Wisconsin, guest hosts this episode of Field Notes. Guolong talks with UW-Madison Horticulture Professor and Extension Specialist Jed Colquhoun about the use of cover crops to reduce nutrient runoff in canning and processing vegetables. For the farmer perspective, he chats with John Ruzicka of Guth Farms in Bancroft, Wisconsin and Dylan Moore, a Seneca Foods Field Representative, about Guth Farm’s journey in integrating no-till and cover crops into their processing vegetable rotations.
”Nitrogen Leaching in Central Sands: Regional & Field-based Estimation.” This webinar had two speakers, Guolong Liang (outreach specialist in UW-Extension’s Ag water quality program) and Emily Marrs Heineman (graduate student within the Nelson Institute of Environmental Studies, UW-Madison).
Historically, reduced tillage, defined here as tillage that maintains plant surface residue and where nutrients are surface applied (i.e. no-till, zone, strip, or vertical tillage), were touted as the solution for phosphorus loss from agricultural fields.
Nitrate loads to groundwater have increased statewide, with studies estimating that over 10% of private wells in Wisconsin exceed the health standard of 10 mg/L (Wisconsin Groundwater Council 2022). In areas with over 75% agricultural land use, the percentage of private wells exceeding the standard increases to 20%.
Farms with livestock have the unique advantage of being able to supply manure, which has many of the nutrients required for crop production, to their fields. However, the application of manure also comes with potential risks to water quality.
Winter Webinar Series 2 of 3 – “Soil test phosphorus: an important risk factor for water quality.” This webinar had two speakers, Chelsea Zegler (an outreach specialist in UW-Extension’s Ag water quality program) and Dr. Jamie Patton (regional specialist with UW-Madison’s Nutrient and Pest Management Program). This webinar went into depth about the phosphorus (P) cycle, analyzing soil test phosphorus and how it is an important tool to use on farms to limit P losses.
Presenters Laura Paletta (an outreach specialist in UW-Extension’s Ag water quality program) and Dr. Francisco Arriaga (assistant professor in the Dept. of Soil Science at UW-Madison) go into depth looking at the best and worst times to spread manure, why it’s important for water quality, and offer recommendations to help limit soil and nutrient losses.
Amber Radatz, program director for UW-Madison Extension’s Ag water quality program, talks about the positive impacts utilizing multiple best management practices can have on a landscape. It typically takes more than just one conservation practice to make a significant impact. The ultimate goal is to keep soil and nutrients on the field rather than erode […]
This short video shares the best times to spread manure throughout the year, why it’s important to consider various field and weather conditions and offers best management practices to install to reduce soil and nutrient losses.
This article was originally published in The Journal of Nutrient Management Discovery Farms’ Nitrogen Use Efficiency Project provides farmers and agronomists opportunities to evaluate their N management to determine the economic and environmental impacts of current practices. With five growing seasons of data collection and 300 fields in our database, we have established benchmarks for […]